Valence Bond Theory
Valence Bond Theory: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as bonding in coordination compounds, valence bond theory, linear complexes with coordination number 2, tetrahedral complexes with coordination number 4 and square planar complexes with coordination number 4.
Important Questions on Valence Bond Theory
Which of the following plot represents potential energy of a pair of nuclei as a function of their separation:
In which of the following species, the underlined carbon atom is hybridised?
Which is the following has the regular tetrahedral structure?
The state of hybridisation of boron and oxygen atoms in boric acid molecule are respectively –
The number of bonds, bonds and lone pair of electrons in pyridine, respectively.
The species having hybradisation is/are:
How does percentage character afftect the bond angle?
Identify the orbital hybridization at the two indicated carbons in the molecule below:
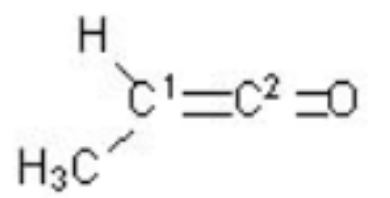
Find the % of orbital in hybridisation.
The molecule which contains and bonds in it is
In which of the following is in the hybridised state.
There are number of bonds and number of bonds present in the compound given below :
The value of is
Match the following.
| Column - I (Compound of ) |
Column - II (Hybridization of ) |
||
| A) | I) | ||
| B) | II) | ||
| C) | III) | ||
| D) | IV) |
The correct match is
Find the number of molecules or ions in which d orbitals is/are not used in hybridisation
A single bond is always a '' bond where as multiple bonds contain bolh and bonds. A double bond contains one and and one bond whereas a triple bond contain one and bonds. On basis of this statement calculate and bonds in .

